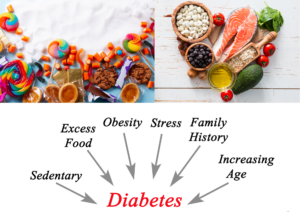
When people think about diabetes, they often associate it with sugar—either eating too much of it or avoiding it entirely. While blood sugar levels play a crucial role in diabetes management, the condition is far more complex.
Diabetes affects multiple organs and systems in the body, leading to serious complications if not properly managed. Understanding diabetes beyond just sugar intake is essential for effective treatment and long-term health.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes glucose, a vital source of energy. It occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or cannot use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels, and without it, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to various health problems.
There are three main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes – An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It requires lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2 Diabetes – A condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough. It is often linked to lifestyle factors, but genetics also play a role.
- Gestational Diabetes – A temporary form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy but increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
For more information about diabetes types, visit the American Diabetes Association.
Diabetes Complications: More Than Just Sugar
While managing blood sugar is a primary focus, diabetes affects the entire body. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to severe complications, including:
1. Heart Disease and Stroke
People with diabetes are at higher risk for heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke. High blood sugar damages blood vessels over time, leading to:
- Hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis)
- Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes
- High cholesterol levels, which further impact heart health
Managing blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle are critical for reducing these risks.
2. Nerve Damage (Diabetic Neuropathy)
Long-term high blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to pain, tingling, or numbness, especially in the hands and feet. Severe cases can result in:
- Loss of sensation in the extremities
- Increased risk of injuries and infections
- Foot ulcers that can lead to amputation
Checking your feet regularly and maintaining proper blood sugar levels can help prevent neuropathy.
3. Kidney Damage (Diabetic Nephropathy)
Diabetes is one of the leading causes of kidney disease. The kidneys work to filter waste from the blood, but high blood sugar can damage their delicate structures over time, leading to:
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Kidney failure, requiring dialysis or transplantation
Routine kidney function tests and staying hydrated can help protect kidney health. Learn more about kidney disease at the National Kidney Foundation.
4. Eye Problems and Vision Loss
Diabetes can damage the small blood vessels in the eyes, leading to conditions such as:
- Diabetic retinopathy – Damage to the retina that can cause blindness if untreated
- Cataracts – Clouding of the eye lens, occurring earlier in diabetics
- Glaucoma – Increased eye pressure that can lead to vision loss
Annual eye exams are essential for early detection and treatment of diabetic eye diseases. For more eye health resources, visit JDRF.
5. Slow Healing Wounds and Infections
Diabetes affects circulation and the immune system, making it harder for wounds to heal properly. Minor cuts or bruises can turn into serious infections, sometimes leading to amputations. Proper foot care and wound management are crucial for preventing complications.
6. Mental Health and Diabetes
The emotional burden of managing diabetes can lead to stress, anxiety, and depression. Many people experience diabetes distress, a condition where managing the disease feels overwhelming. Seeking support from healthcare providers, counselors, or diabetes support groups can help with mental health challenges.
Managing Diabetes Beyond Blood Sugar
While controlling blood sugar is essential, diabetes management involves a holistic approach, including:
1. Healthy Eating Habits
A balanced diet is key to maintaining stable blood sugar levels and overall health. Key dietary tips include:
- Choosing whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats
- Limiting processed foods and sugary beverages
- Eating plenty of fiber-rich vegetables
2. Staying Active
Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Activities like walking, swimming, and strength training can be beneficial.
3. Regular Monitoring and Medication
People with diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly to ensure they stay within a healthy range. If you have extra diabetes supplies, consider selling them through Test Strip Search to help others who need them.
4. Stress Management and Mental Well-being
Managing stress is crucial for diabetes control. Practices like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help regulate stress levels and improve overall health.
Diabetes is not just about sugar—it’s a complex condition that affects multiple organs and systems. By focusing on overall health, from heart and kidney function to mental well-being, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of complications and live fulfilling lives.